Click here to watch in Youtube : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gOX3kvMKrRs&list=UUhwKlOVR041tngjerWxVccw&index=4
Click the below Image to Enlarge
Create Stored Procedure
Click the below Image to Enlarge
.jpg) |
| JDBC - CallableStatement Multiple In Out Parameters (Mysql) |
.jpg) |
| JDBC - CallableStatement Multiple In Out Parameters (Mysql) |
DELIMITER $$ DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS `world`.`getCityInfo` $$ CREATE PROCEDURE `world`.`getCityInfo` (IN CITY_ID_INPUT INT, IN CITY_POPULATION_INPUT INT, OUT CITY_NAME_OUT VARCHAR(255), OUT CITY_COUNTRY_CODE_OUT VARCHAR(255), OUT CITY_DISTRICT_OUT VARCHAR(255), OUT CITY_POPULATION_OUT INT(11)) BEGIN SELECT Name,CountryCode,District,Population INTO CITY_NAME_OUT,CITY_COUNTRY_CODE_OUT,CITY_DISTRICT_OUT, CITY_POPULATION_OUT FROM city WHERE ID = CITY_ID_INPUT AND Population > CITY_POPULATION_INPUT; END $$ DELIMITER ;
set @CITY_ID_INPUT=1; set @CITY_POPULATION_INPUT=1000; call getCityInfo(@CITY_ID_INPUT,@CITY_POPULATION_INPUT,@CITY_NAME_OUT,@CITY_COUNTRY_CODE_OUT, @CITY_DISTRICT_OUT,@CITY_POPULATION_OUT); select @CITY_NAME_OUT,@CITY_COUNTRY_CODE_OUT,@CITY_DISTRICT_OUT,@CITY_POPULATION_OUT;
import java.sql.CallableStatement; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.util.Scanner; public class JDBCCallableStatementDemo { // JDBC driver name and database URL static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/world"; // Database credentials static final String USERNAME = "root"; static final String PASSWORD = "root"; public static void main( String[] args ) { JDBCCallableStatementDemo jdbcCallableStatementDemo = new JDBCCallableStatementDemo(); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); while( true ) { System.out.print("Enter City Id :"); int cityId = scanner.nextInt(); System.out.print("Enter City population :"); int population = scanner.nextInt(); if( cityId == 0 && population == 0) { break; } jdbcCallableStatementDemo.getCityInfo(cityId,population); } scanner.close(); } private void getCityInfo( int cityId , int population ) { Connection connection = null; CallableStatement callableStatement = null; try { /* * Register the JDBC driver in DriverManager */ Class.forName(JDBC_DRIVER); /* * Establish connection to the Database using DriverManager */ connection = DriverManager .getConnection(DB_URL, USERNAME, PASSWORD); String plSql = "{call getCityInfo (?,?,?,?,?,?)}"; callableStatement = connection.prepareCall(plSql); /* * Bind IN parameter first, then bind OUT parameters */ callableStatement.setInt(1, cityId); callableStatement.setInt(2, population); /* * Register OUT Parameters */ callableStatement.registerOutParameter(3, java.sql.Types.VARCHAR); callableStatement.registerOutParameter(4, java.sql.Types.VARCHAR); callableStatement.registerOutParameter(5, java.sql.Types.VARCHAR); callableStatement.registerOutParameter(6, java.sql.Types.INTEGER); /* * Use execute method to run the stored procedure. */ callableStatement.execute(); /* * Retrieve cityName,countryCode,district and cityPopulation with getXXX method */ String cityName = callableStatement.getString(3); String countryCode = callableStatement.getString(4); String district = callableStatement.getString(5); int cityPopulation = callableStatement.getInt(6); System.out.println("city Name : " + cityName+", countryCode : " +countryCode +", district : "+district+", population : "+cityPopulation); } catch( SQLException se ) { se.printStackTrace(); } catch( ClassNotFoundException e ) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch( Exception e ) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { /* * finally block used to close resources */ try { if( callableStatement != null ) { callableStatement.close(); } } catch( SQLException sqlException ) { sqlException.printStackTrace(); } try { if( connection != null ) { connection.close(); } } catch( SQLException sqlException ) { sqlException.printStackTrace(); } } } }
Enter City Id :1 Enter City population :1000 city Name : Kabul, countryCode : AFG, district : Kabol, population : 1780000 Enter City Id :0 Enter City population :0
https://sites.google.com/site/javaee4321/jdbc/JDBCCallableStatementDemoMultipleInOutParamsMysqlApp.zip?attredirects=0&d=1
See also:

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
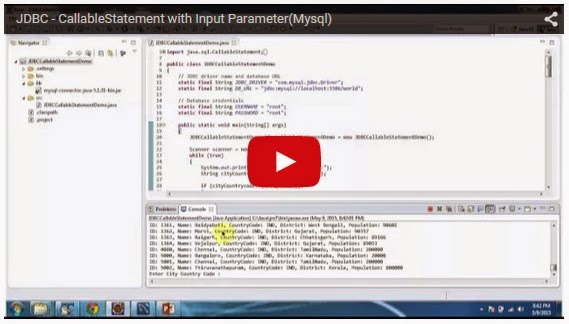.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)















