Click here to watch in Youtube :
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6cE7lbJK7_U&list=UUhwKlOVR041tngjerWxVccw
Click the below Image to Enlarge
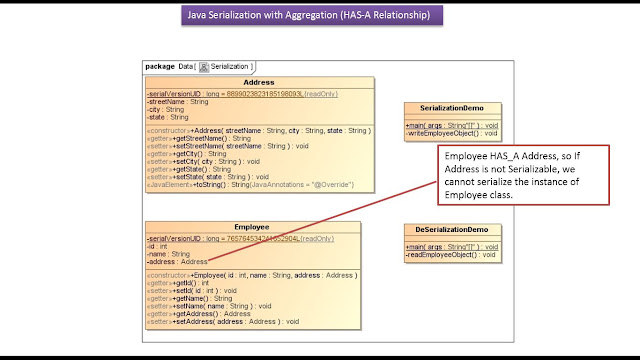 |
| Java Tutorial : Java IO (Java Serialization with HAS A Inheritance) |
import java.io.Serializable; public class Address implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 8899023823185198093L; private String streetName; private String city; private String state; public Address(String streetName, String city, String state) { super(); this.streetName = streetName; this.city = city; this.state = state; } public String getStreetName() { return streetName; } public void setStreetName(String streetName) { this.streetName = streetName; } public String getCity() { return city; } public void setCity(String city) { this.city = city; } public String getState() { return state; } public void setState(String state) { this.state = state; } @Override public String toString() { return "Address [streetName=" + streetName + ", city=" + city + ", state=" + state + "]"; } }
import java.io.Serializable; /* * If a class has a reference of another class, all the * references must be Serializable otherwise * serialization process will not be performed. In such * case, NotSerializableException is thrown at runtime. * * If Address is not Serializable, we cannot serialize * the instance of Employee class. */ public class Employee implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 765764534241652904L; private int id; private String name; private Address address; // HAS-A public Employee(int id, String name, Address address) { super(); this.id = id; this.name = name; this.address = address; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Address getAddress() { return address; } public void setAddress(Address address) { this.address = address; } }
import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; public class SerializationDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException { SerializationDemo serializationDemo = new SerializationDemo(); serializationDemo.writeEmployeeObject(); } private void writeEmployeeObject() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException { FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null; ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = null; try { fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("employee.tmp"); objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOutputStream); Address address = new Address("North Street", "Chennai", "Tamil Nadu"); Employee employee = new Employee(101, "Peter", address); /* * Write the specified object to the * ObjectOutputStream. */ objectOutputStream.writeObject(employee); System.out .println("Successfully written employee object to the file.\n"); } finally { if (objectOutputStream != null) { /* * Closing a ObjectOutputStream will also * close the OutputStream instance to which * the ObjectOutputStream is writing. */ objectOutputStream.close(); } } } }
Successfully written employee object to the file.employee.tmp
DeSerializationDemo.java
import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; public class DeSerializationDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException { DeSerializationDemo deSerializationDemo = new DeSerializationDemo(); deSerializationDemo.readEmployeeObject(); } private void readEmployeeObject() throws IOException, FileNotFoundException, ClassNotFoundException { FileInputStream fileInputStream = null; ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = null; try { fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("employee.tmp"); objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(fileInputStream); /* * Read an object from the ObjectInputStream. */ Employee employee = (Employee) objectInputStream.readObject(); System.out .println("Successfully read employee object from the file."); System.out.println("Id = " + employee.getId()); System.out.println("Name = " + employee.getName()); Address address = employee.getAddress(); System.out.println("Address = " + address); } finally { if (objectInputStream != null) { /* * Closing a ObjectInputStream will also * close the InputStream instance from which * the ObjectInputStream is reading. */ objectInputStream.close(); } } } }
Successfully read employee object from the file. Id = 101 Name = Peter Address = Address [streetName=North Street, city=Chennai, state=Tamil Nadu]
https://sites.google.com/site/ramj2eev1/home/javabasics/JavaIODemo_Serialization_HAS_A_Relationship_App.zip?attredirects=0&d=1
Github Link:
https://github.com/ramram43210/Java/tree/master/BasicJava/JavaIODemo_Serialization_HAS_A_Relationship_App
Bitbucket Link:
https://bitbucket.org/ramram43210/java/src/9ef303db3f229fc70e7cf47baac5692282611e62/BasicJava/JavaIODemo_Serialization_HAS_A_Relationship_App/?at=master
See also:



No comments:
Post a Comment