Click here to watch in Youtube :
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DOaZ0f6vGCE&list=UUhwKlOVR041tngjerWxVccw
Click the below Image to Enlarge
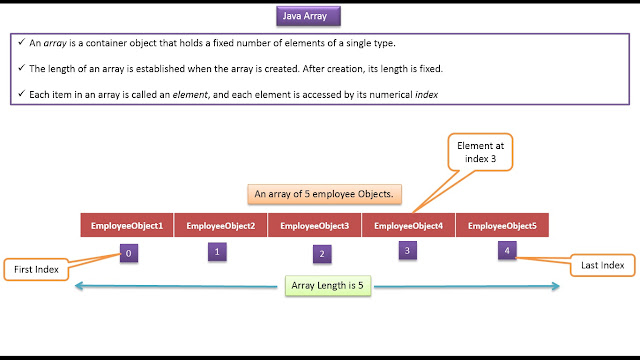 |
| Java Tutorial : Java Array (User Defined Object) |
public class Employee { private String name; private int age; private int salary; public Employee(String name, int age, int salary) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; this.salary = salary; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public int getSalary() { return salary; } public void setSalary(int salary) { this.salary = salary; } @Override public String toString() { return "Employee [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", salary=" + salary + "]"; } }
class ArrayDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { /* * declares an array of Employee Objects and allocates memory for 5 * Employee Objects */ Employee[] employeeArray = new Employee[5]; // initialize first element employeeArray[0] = new Employee("Peter", 23, 60000); // initialize second element employeeArray[1] = new Employee("John", 33, 66000); // and so forth employeeArray[2] = new Employee("Ram", 31, 90000); employeeArray[3] = new Employee("David", 24, 40000); employeeArray[4] = new Employee("Stephan", 45, 95000); int i = 0; for (Employee employee : employeeArray) { System.out.println("Element at index " + i + " : " + employee); ++i; } } }
Element at index 0 : Employee [name=Peter, age=23, salary=60000] Element at index 1 : Employee [name=John, age=33, salary=66000] Element at index 2 : Employee [name=Ram, age=31, salary=90000] Element at index 3 : Employee [name=David, age=24, salary=40000] Element at index 4 : Employee [name=Stephan, age=45, salary=95000]
https://sites.google.com/site/javaee4321/java/ArrayDemoUserDefinedApp.zip?attredirects=0&d=1
See also:


No comments:
Post a Comment